How to Build a High-Performance Project Management Office (PMO)
By Shubhangi Pandey | 10 Min Read | Updated November 25, 2024
In today’s fast-paced and complex business landscape, delivering successful projects is critical to achieving strategic goals. A Project Management Office (PMO) serves as a centralized hub within an organization, designed to standardize processes, improve project execution, and align initiatives with the organizations strategic business goals.
Modern organizations need PMOs and scalable project management tools such as BrightWork 365 more than ever to handle increasing project complexity, improve cross-departmental collaboration, and respond quickly to market changes. A high-performing PMO not only drives project success but also empowers businesses to innovate and stay competitive in a dynamic environment.
Introduction to a Project Management Office (PMO)
What is a PMO?
A Project Management Office (PMO) is a centralized function within an organization that establishes and enforces standards, practices, and governance for managing projects. The PMO acts as the backbone of an organization’s project management efforts, ensuring that projects are executed efficiently, align with strategic objectives, and deliver tangible business value.
Key purposes of a PMO include:
- Governance: Setting policies, standards, and frameworks to ensure projects comply with organizational objectives.
- Support: Providing resources, templates, tools, and training to project teams to enhance their efficiency.
- Alignment: Bridging the gap between business strategy and project execution to ensure every project contributes to organizational goals.
Types of PMOs
PMOs can take various forms depending on an organization’s needs, culture, and project management maturity. The three main types of PMOs are:
- Supportive PMO
- Provides advisory services and tools to project teams without enforcing compliance.
- Best for organizations with a low level of project management maturity or those transitioning to a structured project management environment.
- Key offerings: Templates, training, best practices, and documentation support.
- Controlling PMO
- Establishes methodologies, frameworks, and compliance requirements for project execution.
- Works well in organizations seeking consistency and standardization across projects.
- Mandates adherence to project management practices, balancing flexibility with governance.
- Directive PMO
- Assumes full control over projects, assigning project managers and overseeing execution from start to finish.
- Ideal for organizations with highly complex or mission-critical projects where consistency and accountability are non-negotiable.
- Direct involvement ensures alignment with organizational strategy and resource optimization.
Selecting the right type of PMO depends on the organization’s culture, level of project management maturity, and the strategic role of projects in achieving business objectives.
Benefits of Establishing a PMO
Improved Project Success Rates
A well-structured PMO significantly improves the success rates of projects by:
- Better Planning: Ensuring that projects start with a clear roadmap, defined objectives, and measurable deliverables.
- Risk Management: Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks early to avoid disruptions during execution.
- Resource Allocation: Aligning the right people, tools, and budgets with project requirements, reducing delays and inefficiencies.
Enhanced Strategic Alignment
PMOs bridge the gap between strategy and execution by:
- Prioritizing Projects: Ensuring that only projects aligned with business goals receive approval and resources.
- Tracking Value Delivery: Monitoring project progress and outcomes to verify they align with the intended strategic value.
- Facilitating Decision-Making: Providing executives with data-driven insights to prioritize initiatives and allocate resources effectively.
Resource Optimization and Cost Savings
PMOs help organizations make the most of their resources by:
- Centralizing Resource Management: Preventing resource conflicts and underutilization by dynamically allocating resources across projects.
- Avoiding Project Overlaps: Establishing a holistic view of all projects to eliminate redundancies and inefficiencies.
- Controlling Budgets: Monitoring financial performance, detecting variances, and recommending corrective actions to avoid cost overruns.
Better Stakeholder Communication
Effective communication is critical for project success, and a PMO ensures transparency and engagement by:
- Centralizing Communication Channels: Acting as the single source of truth for project status, updates, and deliverables.
- Providing Regular Reports: Offering real-time dashboards and periodic status reports tailored to stakeholder needs.
- Facilitating Stakeholder Engagement: Ensuring that executives, sponsors, and team members remain informed and aligned on project priorities and expectations.
PMO Roles and Responsibilities
A successful Project Management Office (PMO) relies on well-defined roles and responsibilities to support its core mission of delivering project success and aligning with organizational strategy. Here, we break down the key functions, roles, and skills essential for a high-performance PMO.
Core Functions of a PMO
- Project Support
- Assist project teams with tools, templates, and best practices to streamline execution.
- Provide troubleshooting and guidance for overcoming challenges during the project lifecycle.
- Governance
- Establish and enforce project policies, processes, and compliance standards.
- Ensure project activities adhere to organizational strategies, budgets, and risk thresholds.
- Conduct periodic audits and reviews to ensure alignment and accountability.
- Methodology Standardization
- Develop and implement standardized project management methodologies (e.g., Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid).
- Ensure uniformity in how projects are initiated, planned, executed, and closed, improving efficiency and consistency.
- Training and Capability Building
- Offer training programs to develop project management skills among team members.
- Stay updated on industry trends and integrate new methodologies, tools, and practices into the organization.
- Resource Management
- Act as a central hub for resource allocation, ensuring optimal utilization across multiple projects.
- Forecast resource demand and resolve conflicts to maintain smooth project execution.
By focusing on these functions, a PMO ensures projects are delivered on time, within scope, and aligned with organizational goals.
PMO Roles and Titles
A PMO is staffed by professionals with diverse expertise, each playing a critical role in achieving the PMO’s objectives. Key roles include:
- PMO Director
- Responsible for the overall strategy, direction, and performance of the PMO.
- Collaborates with executives to align projects with organizational goals.
- Oversees team performance, budget management, and resource planning.
- Project Managers
- Directly manage individual projects, ensuring they are executed on time, within budget, and to scope.
- Act as the primary point of contact for stakeholders, resolving issues and maintaining progress.
- Portfolio Managers
- Oversee a collection of projects and programs to ensure they align with organizational priorities.
- Evaluate project proposals and allocate resources based on strategic value and ROI.
- Analysts (Project or PMO Analysts)
- Collect and analyze project data to identify trends, risks, and improvement opportunities.
- Develop reports and dashboards that provide stakeholders with actionable insights.
- PMO Coordinators
- Handle administrative tasks such as scheduling meetings, updating project documentation, and tracking deadlines.
- Ensure seamless communication and coordination across teams and stakeholders.
These roles work together to deliver efficient project execution while maintaining alignment with strategic goals.
PMO Frameworks and Methodologies
A robust framework and the right methodology are the cornerstones of a successful Project Management Office (PMO). These elements provide structure, consistency, and a clear approach to managing projects, portfolios, and programs effectively while aligning them with organizational objectives.
Purpose of a PMO Framework
A PMO framework acts as a strategic blueprint that defines how projects are planned, executed, monitored, and closed within an organization. It ensures that all project management activities align with business goals and deliver maximum value.
Key benefits of a PMO framework include:
- Standardization: Establishing consistent practices and processes across projects.
- Efficiency: Reducing redundancies and inefficiencies by following a structured approach.
- Governance: Enforcing compliance with organizational policies and external regulations.
- Scalability: Providing a flexible structure that can adapt as the organization grows.
Common PMO Methodologies
Waterfall Methodology
The Waterfall Methodology is a traditional, sequential approach where each project phase, such as requirements, design, development, and testing, must be completed before moving to the next. This methodology is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and minimal expected changes and is commonly used in industries like construction, manufacturing, and aerospace.
Advantages:
- Clear structure and deliverables.
- Predictable timelines and costs.
- Easy to manage and monitor progress.
Limitations:
- Limited flexibility to adapt to changes.
- Not ideal for projects with evolving requirements.
Agile Methodology
A flexible, iterative approach that delivers work in smaller increments called sprints, allowing teams to adapt to change and incorporate feedback quickly. This methodology is popular in software development, IT, and industries that prioritize innovation and responsiveness.
Advantages:
- Increased flexibility and faster delivery.
- Greater collaboration and customer involvement.
- Early identification and resolution of issues.
Limitations:
- Requires significant stakeholder engagement.
- May lack the structure of traditional methods.
Hybrid Methodology
Hybrid methodology combines elements of Waterfall and Agile, offering the predictability of Waterfall for some aspects and the flexibility of Agile for others. This methodology is ideal for organizations with diverse projects or teams requiring a balance between structure and adaptability.
Advantages:
- Flexibility to tailor the approach to project needs.
- Enables teams to adopt best practices from both methodologies.
Limitations:
- Can be complex to implement and manage.
Lean Methodology
Lean project management methodology focuses on delivering maximum value to customers while minimizing waste and inefficiencies. Lean methodology is frequently used in manufacturing, but its principles apply across industries.
Advantages:
- Emphasizes efficiency and resource optimization.
- Promotes continuous improvement.
Limitations:
- Can be challenging to identify and eliminate inefficiencies without expert guidance.
PMI and PRINCE2 Frameworks
PMI (Project Management Institute): Offers guidelines and certifications (e.g., PMP) that emphasize standardized practices and techniques.
PRINCE2 (Projects in Controlled Environments): A highly structured methodology that focuses on defined roles, governance, and processes for complex projects.
Advantages:
- Clear governance and accountability.
- Scalable and adaptable for diverse projects.
Limitations:
- Can be rigid and require extensive documentation.
Selecting the Right Methodology for Your PMO
Here are five factors to consider when you are selecting a project management methodology for your PMO:
- Project Complexity: Simple projects may benefit from Waterfall, while Agile is better for dynamic, complex projects.
- Industry Type: Manufacturing may prefer Lean or Waterfall, whereas IT and software development often use Agile.
- Organizational Goals: Choose a methodology that aligns with business priorities, whether it’s speed, innovation, or cost control.
- Team Expertise: Consider the team’s familiarity with methodologies; training may be needed for newer approaches.
- Stakeholder Preferences: Ensure stakeholders are comfortable with the level of involvement and reporting.
Aligning Frameworks with PMO Objectives
By aligning frameworks with the PMO’s objectives and investing in ongoing skill development, organizations can enhance project outcomes and stay competitive in a rapidly changing environment. This structured approach to frameworks and methodologies ensures that the PMO remains efficient, consistent, and adaptable while supporting the organization’s overarching goals.
Strategic Alignment
To ensure the PMO delivers value PMO leads need to select methodologies that support the organization’s vision and goals. Use data and analytics to measure how well projects contribute to strategic objectives.
Importance of Training and Continuous Education
- Provide regular training to PMO staff on evolving frameworks and tools.
- Stay updated on emerging methodologies (e.g., Scaled Agile Framework, or SAFe).
- Foster a culture of learning to keep the PMO adaptable and forward-looking.
7 Key Steps to Building a High-Performance PMO
A successful PMO is built on a strong foundation of strategic alignment, well-defined processes, and a skilled team. Below, we detail the key steps to establish a PMO that delivers measurable value to your organization.
Step 1: Define the PMO’s Purpose and Objectives
The first step is to clearly articulate why the PMO is being established and what it aims to achieve. This involves close collaboration with executive leadership to align on goals.
Key actions:
- Identify Strategic Priorities: Determine how the PMO will contribute to organizational objectives, such as improving project delivery, enhancing efficiency, or driving innovation.
- Define Scope: Decide whether the PMO will oversee individual projects, programs, or entire portfolios.
- Create a Mission Statement: Develop a clear and concise statement that communicates the PMO’s purpose to all stakeholders.
Outcome: A well-defined mission and set of objectives that align with the company’s strategic goals, serving as a guidepost for the PMO’s operations.
Step 2: Select the Right PMO Structure
Choosing the appropriate PMO structure ensures that it integrates seamlessly with the organization’s culture and needs. You must define the scope of your project management e.g. see if you need a PMO to work at the whole enterprise level, departmental level or at the Individual project/program level. Then, you can go for one of the following types of PMOs based on your organizational goals and project management needs:
Supportive PMO: Provides tools, templates, and guidance but allows teams flexibility. Ideal for organizations with a low level of project management maturity.
Controlling PMO: Establishes processes and ensures compliance with standards. Suitable for organizations seeking more consistency.
Directive PMO: Takes full control of projects and assigns project managers. Works best in highly structured environments or industries with critical compliance requirements.
Key Considerations:
- Assess the organization’s current project management maturity.
- Align the structure with business needs and the degree of oversight required.
- Be prepared to evolve the PMO structure as the organization grows.
Outcome: A tailored PMO structure that matches organizational demands and fosters efficiency.
Step 3: Secure Executive Buy-In and Resources
Executive support is critical to ensure the PMO has the authority and resources it needs to succeed.
Tips for Gaining Buy-In:
- Present a Business Case: Highlight how the PMO will address current challenges, improve project success rates, and drive ROI.
- Show Evidence: Use data, case studies, or benchmarking to demonstrate the value of PMOs in similar organizations.
- Emphasize Alignment: Reinforce how the PMO will help achieve strategic goals.
Securing Resources:
- Advocate for necessary funding, staffing, and technology investments.
- Identify champions within the leadership team to advocate for the PMO’s initiatives.
Outcome: A strong foundation of leadership support and allocated resources to ensure the PMO’s success.
Step 4: Develop Key PMO Processes and Frameworks
Standardized processes and frameworks ensure consistency and scalability across projects. A PMO should involve stakeholders in defining processes to ensure they are practical and widely adopted. A PMO should also aim at keeping processes flexible enough to adapt to different project types.
Key Components to Establish:
- Project Lifecycle Processes: Define the stages of project management (initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure).
- Governance Framework: Set policies and guidelines to ensure compliance with organizational objectives.
- Documentation Standards: Create templates and guidelines for key deliverables like project charters, risk registers, and status reports.
Outcome: A set of clearly documented processes and frameworks that drive efficiency and consistency.
Step 5: Implement Tools and Technology
The right tools and technology enable the PMO to operate efficiently and provide valuable insights. It is ideal to choose tools that integrate with existing systems to reduce complexity. PMOs and PMO leads must invest in providing training to ensure the team uses the tools effectively.
Essential PMO Tools:
- Project Management Software: Tools like Microsoft Project, Asana, or Jira to plan, track, and manage tasks.
- Reporting and Dashboards: Platforms like Power BI or Tableau for real-time performance monitoring.
- Resource Management Systems: Tools to allocate and optimize team resources across projects.
- Collaboration Tools: Platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack to enhance communication and teamwork.
Outcome: A tech-enabled PMO that enhances productivity, visibility, and decision-making.
Step 6: Recruit and Train the Right Talent
The success of a PMO depends on the expertise and capabilities of its team.
Recruitment Strategies:
- Define roles and responsibilities clearly, such as PMO Director, Project Managers, and Analysts.
- Look for candidates with both technical and soft skills, such as leadership, communication, and problem-solving abilities.
Training and Development:
- Offer training on project management methodologies (e.g., Agile, PRINCE2) and tools.
- Encourage certification in recognized standards like PMP or ScrumMaster.
- Foster a culture of continuous learning to adapt to evolving best practices.
Outcome: A skilled and motivated team equipped to deliver PMO objectives effectively.
Step 7: Define Success Metrics and KPIs
To demonstrate value and improve performance, the PMO needs measurable objectives and KPIs. As some of PMO best practices, PMO leads should look at aligning KPIs with the organization’s goals to measure meaningful progress. They must also ensure the use of reporting tools to track and communicate results regularly.
Key Metrics to Track:
- Project Delivery: Percentage of projects delivered on time, within scope, and budget.
- Strategic Alignment: Percentage of projects that align with business goals.
- Resource Utilization: Efficiency in allocating and using resources across projects.
- Stakeholder Satisfaction: Feedback from stakeholders on project outcomes and communication.
Outcome: A clear framework for evaluating and demonstrating the PMO’s value to the organization.
Choosing the Tools and Technology for Your PMO
Equipping your Project Management Office (PMO) with the right tools and technology is essential for streamlining operations, improving decision-making, and driving project success. Below is a breakdown of critical tools and technologies every PMO should consider.
Project Management Software
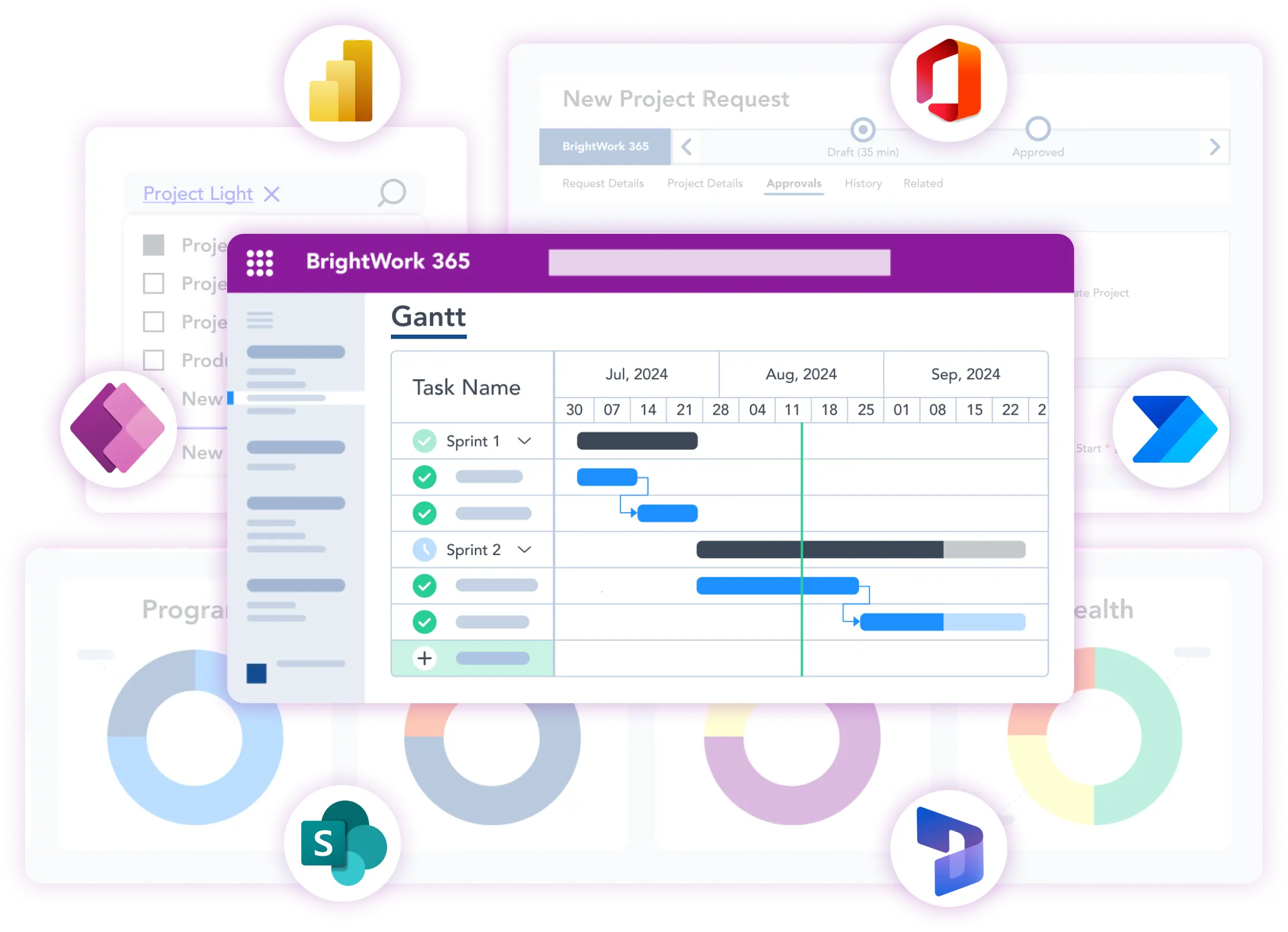
A PMO needs a modern project management solution to help teams plan, execute, and monitor projects effectively by offering features such as task management, timelines, and workflow automation. When choosing a project portfolio management (PPM) software, you need to look at a tool that integrates seamlessly with your organization’s existing systems. PMO leads must also evaluate scalability to ensure the software meets future needs. Tools like BrightWork 365 (built on Microsoft 365 and the Power Platform) offer a complete project portfolio management solution that come with the flexibility of customization, integration, and scale.

Resource Management Tools
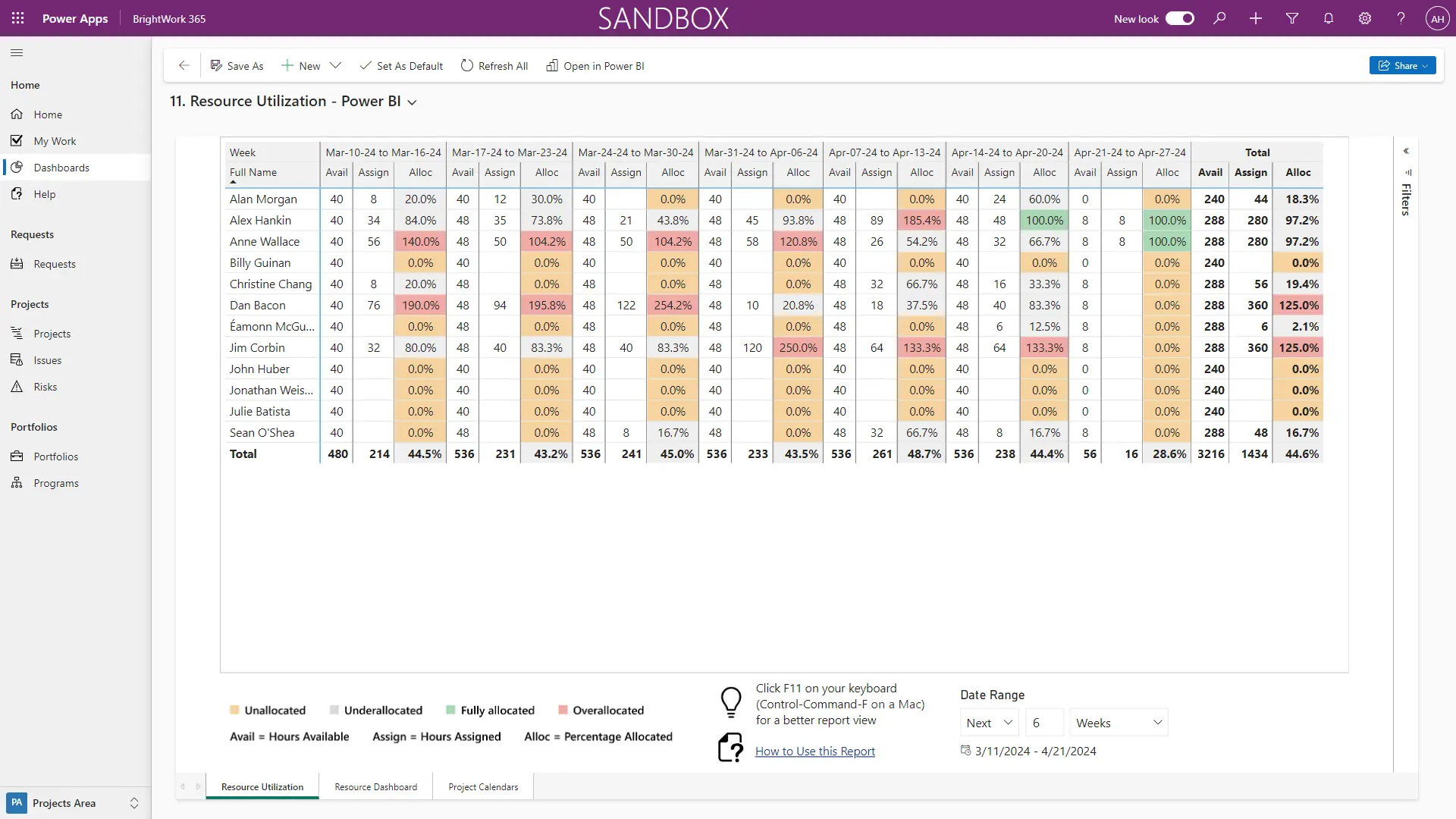
Resource management tools optimize resource allocation, ensuring that personnel, budgets, and materials are effectively utilized across projects. Ensure the tool supports both individual and team-level resource tracking. Look for real-time updates to facilitate dynamic changes in resource allocation.
Key features to look for:
- Scheduling: Visual tools like Gantt charts or calendars to plan resource availability.
- Capacity Planning: Identify bottlenecks or resource shortages before they impact projects.
- Forecasting: Predict future resource needs based on current and upcoming project demands.
Reporting and Analytics Tools
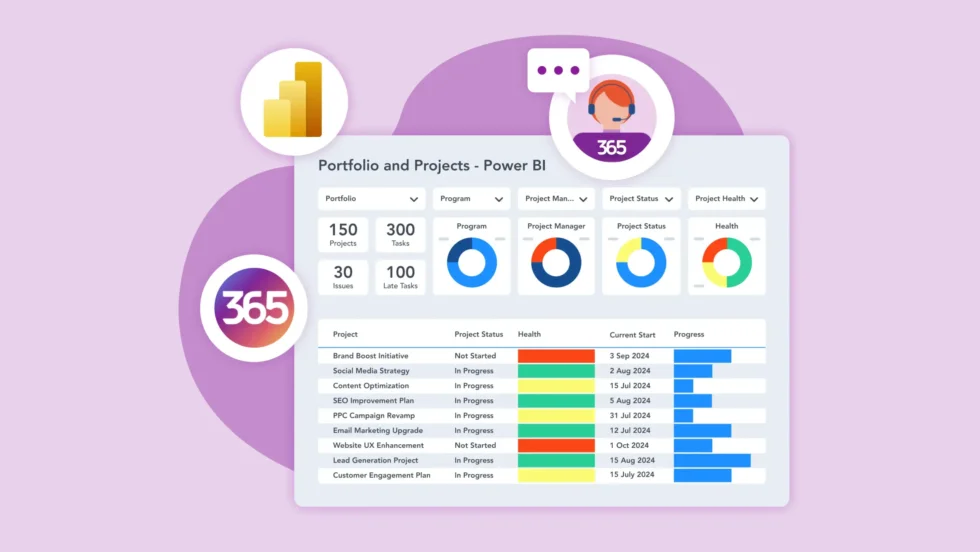
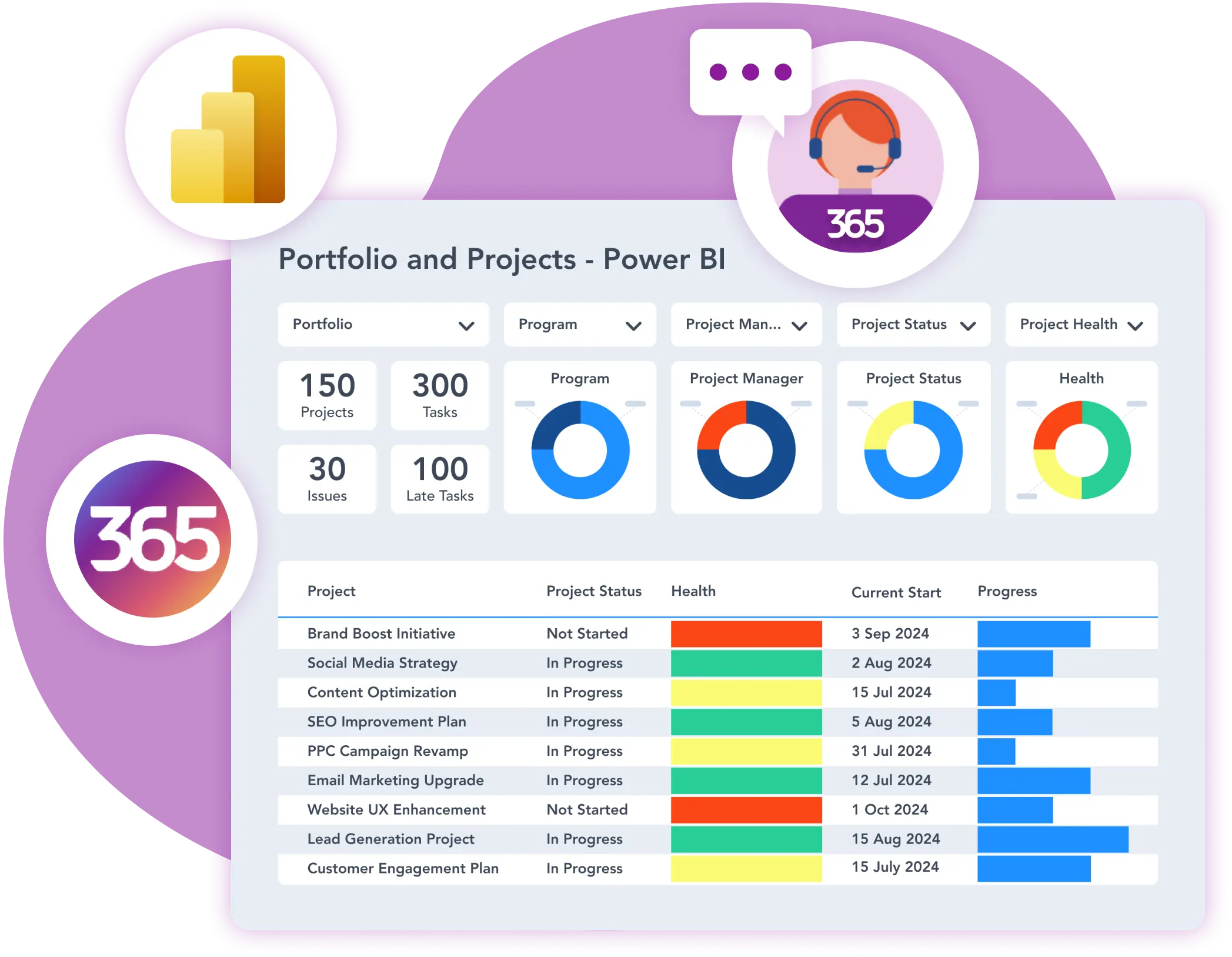
Reporting and analytics tools provide actionable insights by consolidating data across projects and visualizing performance metrics. Ensure the tool supports integration with your project management and resource tools. Focus on tools that enable automation for recurring reports. For example, Power BI is a Microsoft app used for creating visually rich dashboards and reports, with seamless integration with other Microsoft products.
Key features to look for:
- Customizable Dashboards: Allow project managers and executives to track KPIs and metrics that matter most.
- Real-Time Reporting: Keep stakeholders updated with accurate and timely data.
- Data Integration: Combine data from multiple sources for comprehensive analysis.
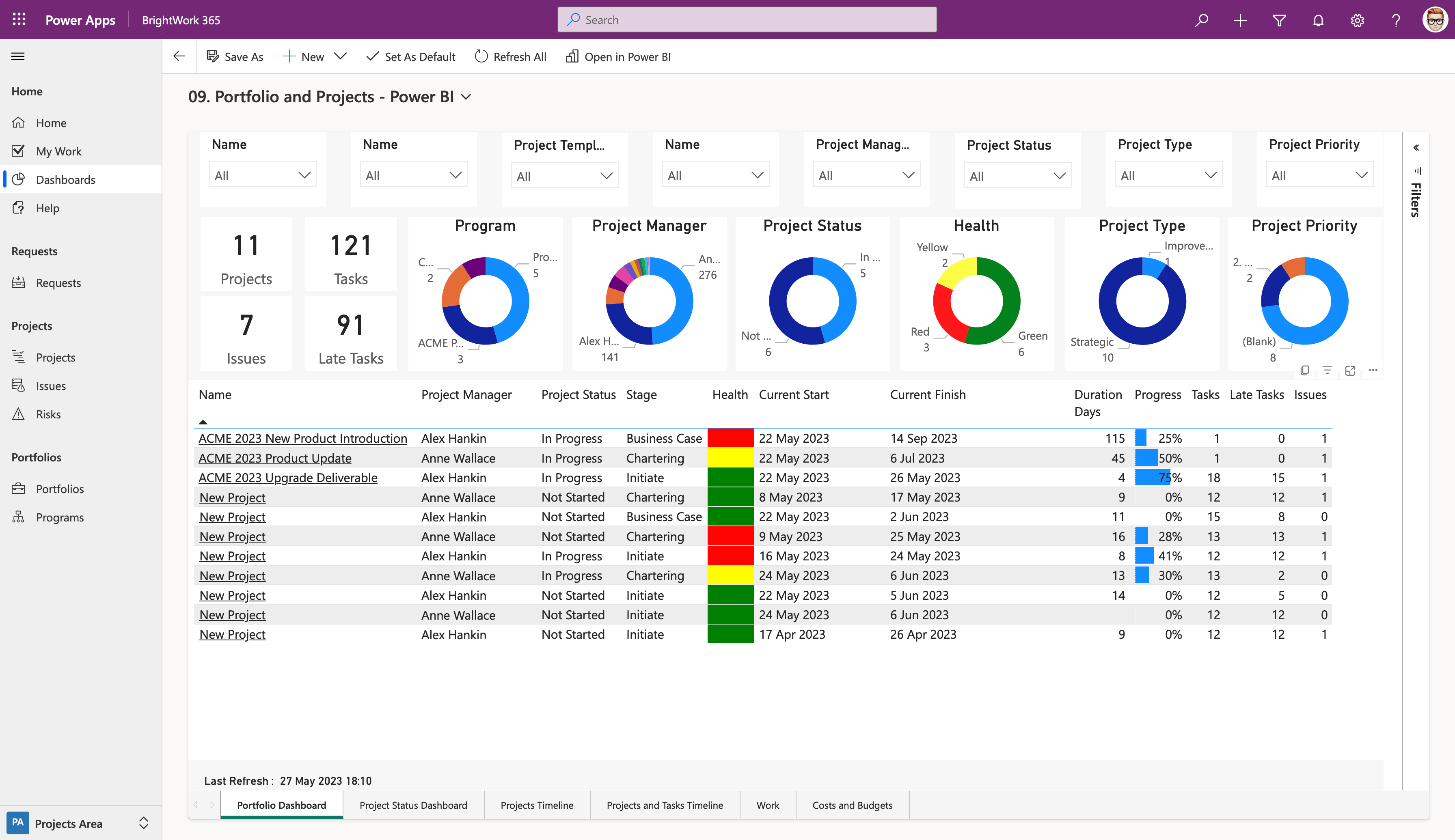
Collaboration and Communication Platforms
Effective communication and collaboration tools are essential for ensuring alignment among team members, stakeholders, and external partners, especially given the rise of hybrid and remote work culture over the last few years. PMOs need to prioritize tools that support both internal team collaboration and external stakeholder engagement. PMOs must ensure the platform aligns with security and compliance requirements, especially for sensitive data. Microsoft Teams, for example, combines chat, video conferencing, and file collaboration with seamless integration into the Microsoft ecosystem.
Key features to look for:
- Instant Messaging: Real-time communication to resolve issues quickly.
- Document Sharing: Centralized platforms for sharing and collaborating on project documents.
- Integration: Tools that work with your project management software and calendars.
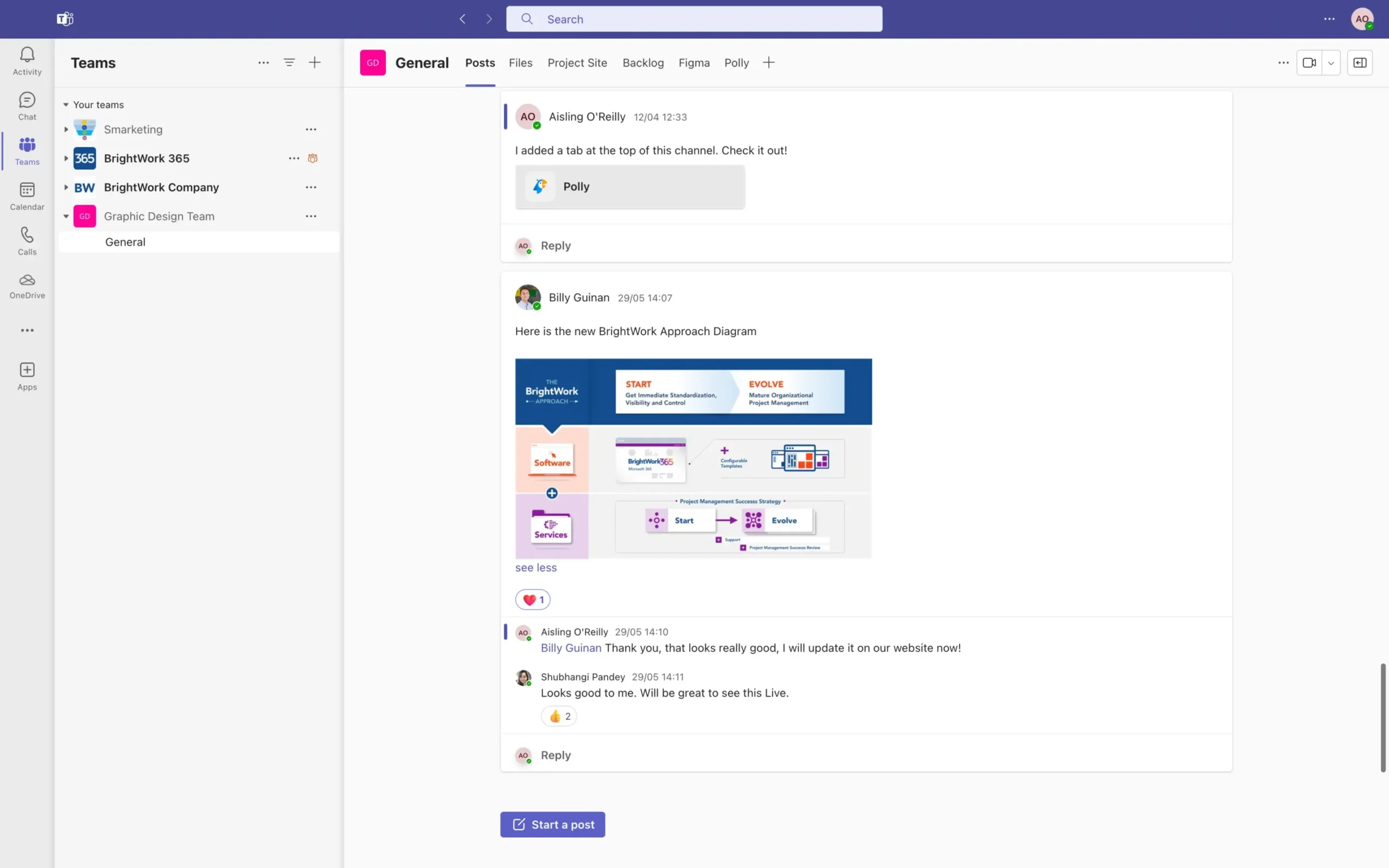
How to Choose the Right Tools for Your PMO
- Assess Organizational Needs: Identify gaps in current processes and prioritize tools that address those challenges.
- Evaluate Scalability: Choose tools that grow with your PMO as project demands increase.
- Focus on Integration: Ensure tools work together to provide a seamless experience across project management, resource allocation, reporting, and collaboration.
- Provide Training: Invest in training sessions to ensure your team utilizes the tools effectively.
By selecting and implementing the right tools, your PMO can enhance efficiency, improve communication, and deliver better outcomes across projects and portfolios.
Scaling Up Your PMO with Microsoft 365 (5 Steps)
Scaling your PMO is essential as your organization grows, project complexity increases, or strategic demands evolve. A high-performing PMO must adapt to these changes to maintain efficiency, alignment, and value delivery. As your PMO matures, scaling its capabilities on the Microsoft 365 platform ensures alignment with organizational growth and evolving project management needs.
Step 1: Assess Current Capabilities and Identify Gaps
Evaluate your PMO’s existing processes, tools, and team skills to identify areas for improvement. Focus on gaps in project tracking, resource allocation, and stakeholder engagement that limit efficiency or scalability.
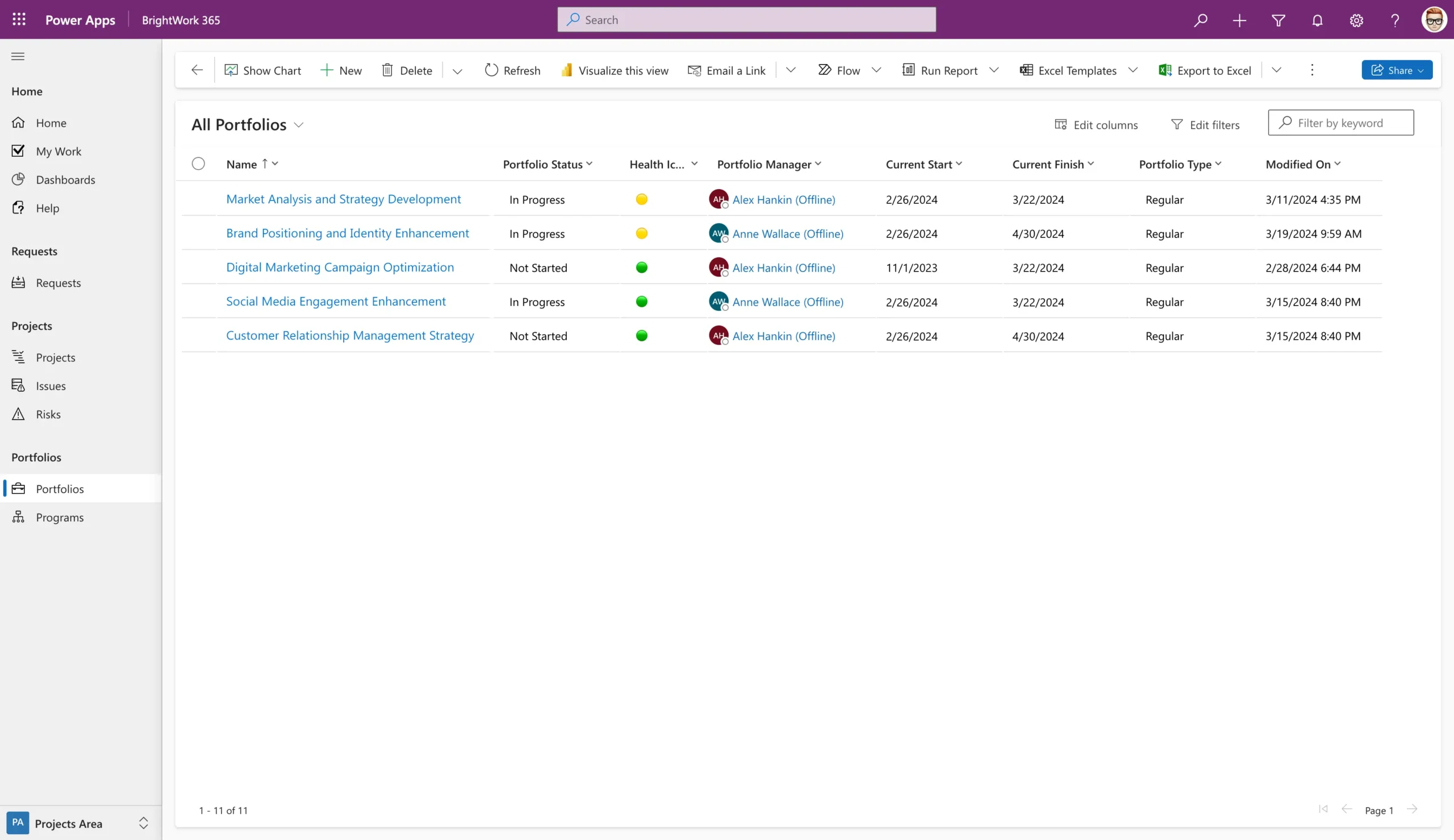
Step 2: Integrate Advanced Project Portfolio Management (PPM) Tools
Leverage tools like BrightWork 365 and Microsoft Project to streamline portfolio management. Use these tools to prioritize projects, optimize resources, and gain real-time insights into portfolio performance to drive better decision-making.
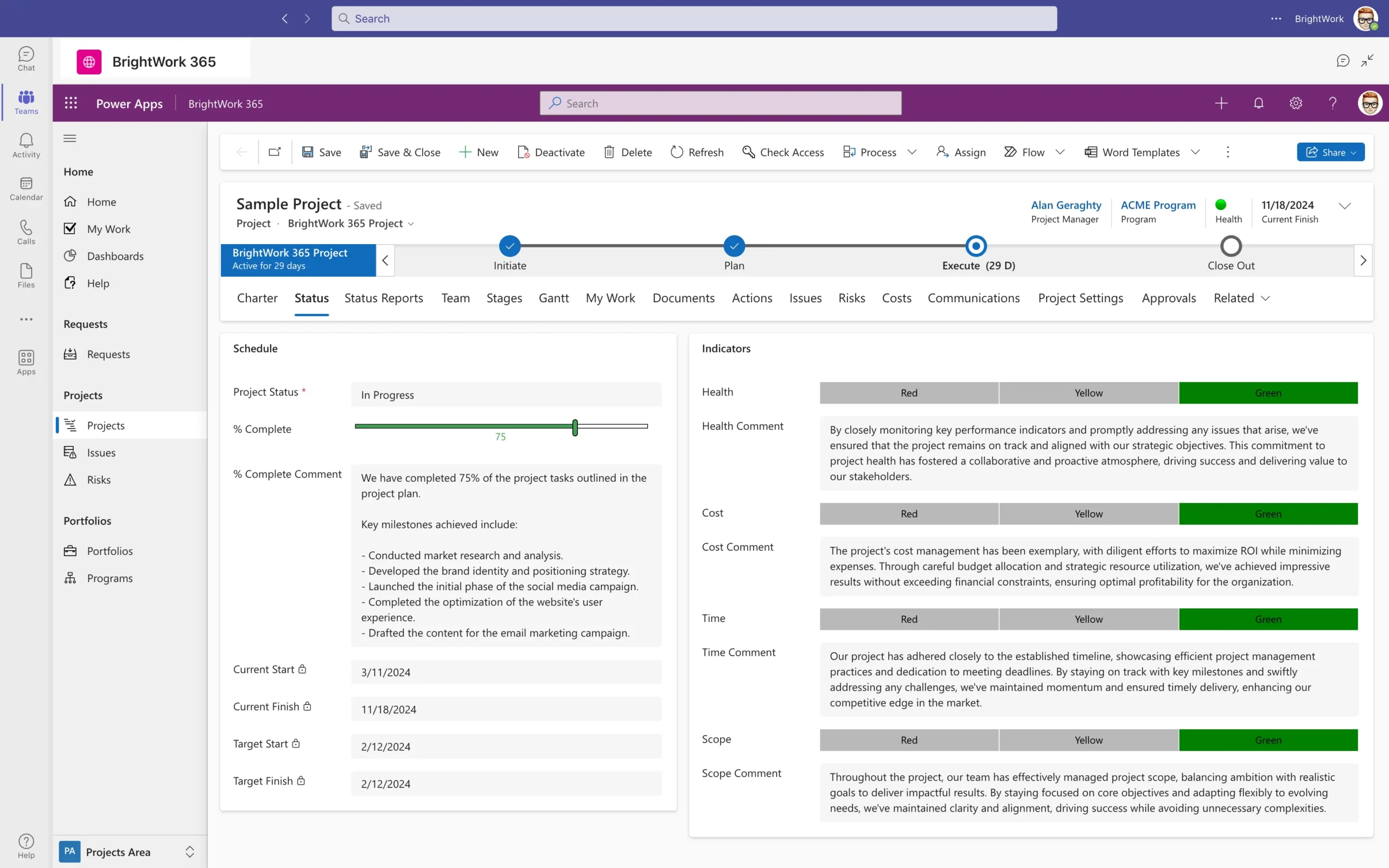
Step 3: Enhance Communication and Collaboration with Microsoft Teams
Maximize the use of Microsoft Teams by creating dedicated channels for projects, integrating Planner for task tracking, and enabling seamless collaboration through SharePoint and OneDrive. Teams also supports integration with BrightWork 365 for enhanced project visibility and updates.
Step 4: Implement Resource Management and Capacity Planning
Use advanced PPM tools like BrightWork 365 for resource management features to allocate resources effectively, track workloads, and balance capacity. This ensures that the right people are working on the right projects without overloading team members.
Step 5: Standardize Reporting and Performance Tracking
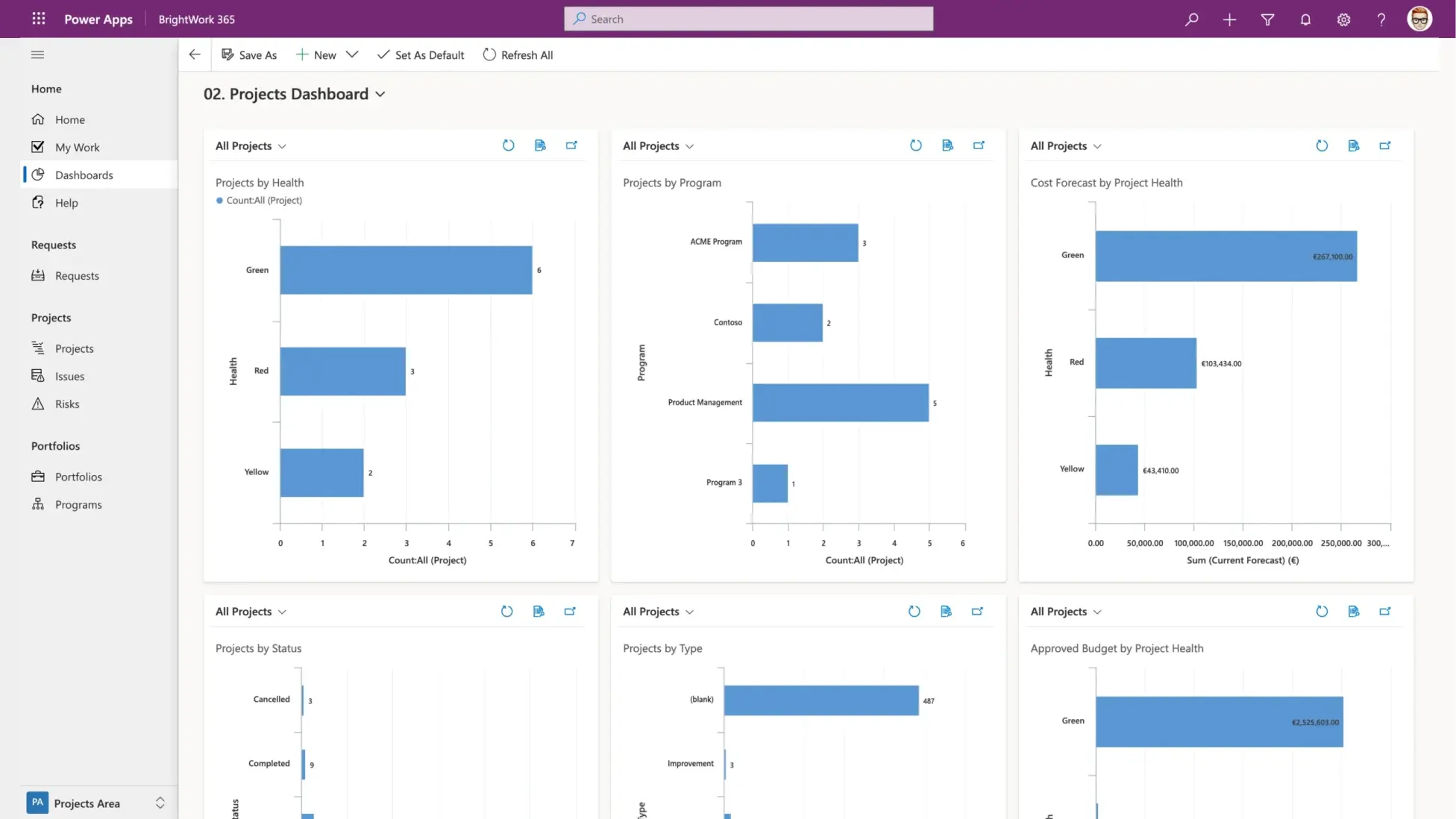
Centralize project and portfolio reporting with Power BI and Power Apps dashboards. Standardized, automated reporting ensures stakeholders have access to consistent, real-time data on project progress, risks, and performance metrics.
PMO Implementation Best Practices
Building a high-performing Project Management Office (PMO) requires more than tools and frameworks—it demands the adoption of strategic practices that ensure efficiency, alignment, and sustained success. The following best practices provide a foundation for effective PMO implementation.
Establish Consistent Processes and Methodologies
Consistency is key to ensuring all projects adhere to established standards and deliver predictable outcomes. Standardization eliminates inefficiencies, fosters trust, and supports a repeatable framework for success. Here’s three ways in which a PMO can bring in consistency.
- Standardized Practices: Define and document core processes such as project initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
- Unified Methodologies: Choose and implement methodologies (e.g., Agile, Waterfall, Hybrid) that align with organizational goals and project types.
- Quality Assurance: Implement review mechanisms to ensure adherence to standards, reducing risks and improving outcomes.
Encourage Continuous Learning and Improvement
A learning-focused culture within the PMO empowers teams to evolve with changing project needs and industry trends. Continuous learning enhances team competence, mitigates future risks, and positions the PMO as a driver of excellence.
- Regular Training: Invest in ongoing training for project managers and team members to develop technical and soft skills.
- Lessons Learned: Conduct post-project reviews to identify successes, challenges, and areas for improvement.
- Agile Mindset: Adopt agile principles to create an environment that embraces experimentation, adapts to feedback, and fosters innovation.
Foster Collaboration and Communication
Effective communication channels and collaborative practices are essential for project success and stakeholder alignment. Strong collaboration improves decision-making, reduces misunderstandings, and ensures everyone is aligned toward shared goals.
- Cross-Departmental Collaboration: Break down silos by creating integrated workflows and shared tools across teams and departments.
- Executive Engagement: Establish clear communication with leadership to align projects with strategic objectives and secure ongoing support.
- Collaboration Tools: Use platforms like Microsoft Teams or Slack to enable seamless communication and real-time updates.
Utilize Data and Analytics for Decision-Making
Data-informed strategies reduce guesswork, improve transparency, and enhance the PMO’s role as a strategic enabler. When PMO Leads use data to make decisions, it helps the PMO prioritize projects, allocate resources, and measure success effectively.
- Dashboards and Reporting: Implement tools like Power BI to create dashboards that track key performance indicators (KPIs) and project health.
- Resource Allocation: Use analytics to monitor workload distribution, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource usage.
- Portfolio Management: Leverage data insights to prioritize projects that align with strategic goals and deliver maximum value.
Setting up a centralized PMO with Microsoft 365
BrightWork 365 leverages Microsoft 365, Power Platform, and Teams to enable PMOs with a centralized project management system.