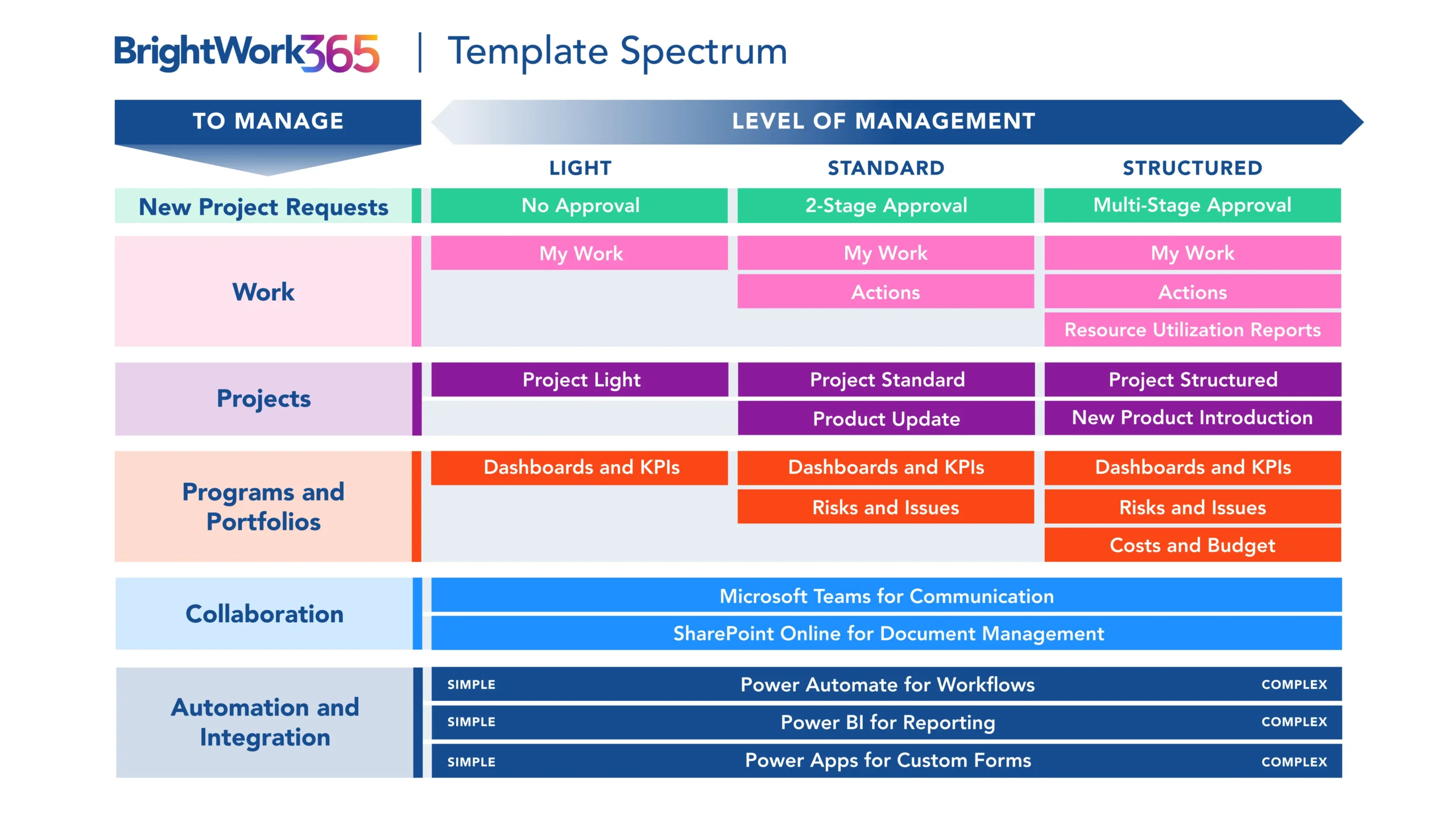
BrightWork 365 enables tracking and reporting of key tasks and statuses, providing visibility and securing buy-in from relevant stakeholders.
Establishing a project management office (PMO) is considered a best practice, which will maximize the outcome.
Optimizing PMOs with BrightWork 365
With the different templates that come with BrightWork 365, you can also establish a PMO with underlying projects reporting rolling up to the project management office. This creates a single source of truth, a significant benefit of having a PMO within an organization.
In addition, BrightWork 365 templates allow the organization’s project management maturity to grow with the creation of a PMO.
How to Set Up a Project Management Office?
In the plan below, the duration of the phases and tasks have been omitted as every Project Management Office (PMO) setup is specific to an organization.
Task durations will depend on the project scope of the PMO role and the readiness of the organization to use the services of a PMO.
Assessment and Strategy Development
The first goal of this activity is to assess the current status of project management and the current project portfolio within the organization.
This assessment is followed by the development of a desired future state and a gap analysis between the current and future states.
-
Assessment
The PMO assessment finds the issues, gaps, challenges, and key decisions to be made.
-
Current Project Portfolio Analysis
This includes carrying out a review of any existing project-based structures and a high-level assessment of the current portfolio of projects.
-
Organizational Culture
This should cover how projects are done today, the perception of project management, and what things are valued.
Establish what existing project management methodology and project governance reporting are in place.
In addition, the stakeholders who will be key to the PMO project’s success should be named.
-
Desired Future State
Outline a desired future state for Project Management based on the assessment findings. This future state should align with strategic goals and support effective project portfolio management.
-
Gap Analysis
Perform a gap analysis between the desired future state and the current state. This analysis will identify pain points and opportunities for improvement and form the basis of the initial PMO Strategy and an Outline Business Case.
-
Approval for Next Phase
The PMO strategy and the Outline Business Case will be submitted to the PMO Steering Committee for approval for the next phase.
This will ensure leadership support for the planned project execution and resources needed for success.
2. Formalizing Project Initiation
Based on approval from the earlier phase, the setup of a PMO will be formalized as a project in this phase.
-
Business Case and PMO Charter
As part of this phase, a business case for the PMO will be completed, as well as a charter for the PMO.
-
Defining PMO Services
A successful PMO will offer a range of services that business units can rely on time after time.
From the outset, the capability to deliver and support such services will not be in place.
The aim of the PMO Charter is to outline the scope of the PMO and what services it will initially offer, setting the stage for effective PMO implementation.
-
Creating the PMO Roadmap
Services have to be introduced gradually, and the PMO roadmap presentation should clearly highlight this, explaining when certain key deliverables will be achieved.
The PMO Roadmap will be ready with input from all stakeholders.
The roadmap will include the rollout scope document that describes the goals, approach, risks, and constraints. It should also be linked to training and change management strategies.
-
Approval to Proceed to Next Phase
Subsequent approval of the Business Case and the PMO Charter by the PMO Steering Committee secure funding for the next phase – the PMO Set-Up and Development Phase.
3. Establishing and Developing the PMO
As part of the approval from the previous stage, the PMO secures funding to set up the PMO and develop the processes and project management tools.
-
Office Establishment
The physical place for the PMO is established, roles are defined, and the PMO staff are appointed to ensure effective setup.
-
Approval for the Next Stage
On completion of the design of PMO key artifacts, training of the project managers, and the completion of the PMO pilots, approval will be sought from the PMO Steering Committee to go to the next phase.
4. Transitioning to PMO Operations
Having fully defined how the PMO will run, projects will be transitioned into the PMO, the planning of which will largely be driven by the outcome of a project review carried out as part of the current situation analysis.
5. Improving PMO Processes
The PMO improves its own operations by measuring effectiveness, adjusting existing services, and adding new ones. It may also need to update its Project Charter.
Additionally, the PMO should assess the overall capability of the organization to deliver acceptable project results on time and within a reliable budget. It can then develop and carry out a long-term plan to strengthen that capability.
Editors note: This post has been updated for freshness, comprehensiveness, and accuracy. This post and One-Page Plan was provided by Ken Martin.
Standardize your project management processes with Microsoft 365
Watch a demo of BrightWork 365 project and portfolio management templates for Microsoft 365, Power Platform, and Teams.